5-13
Cisco AVVID Network Infrastructure Enterprise Quality of Service Design
956467
Chapter 5 QoS in a SOHO Virtual Private Network for IP Telephony
Solutions
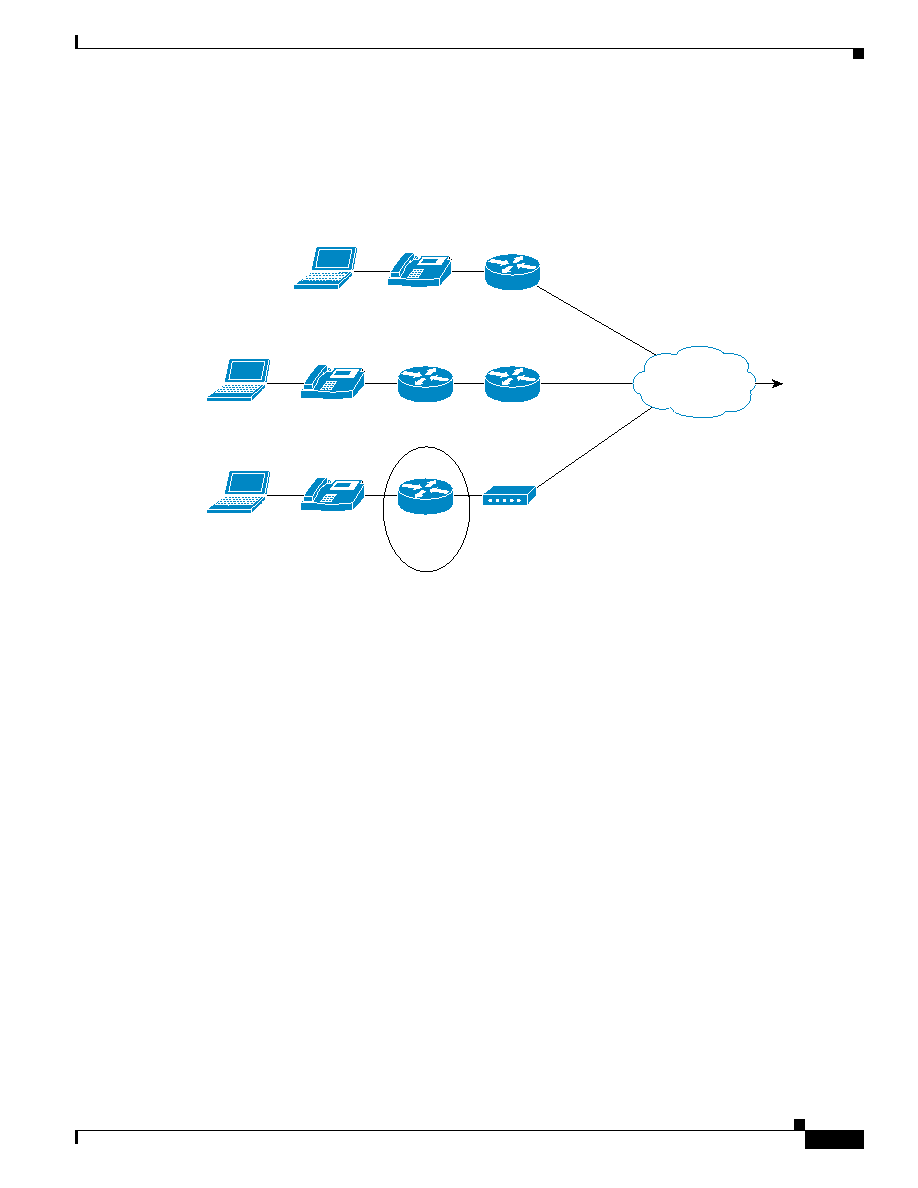
Third-Party Modem Solution
In environments where the cable termination device is not QoS capable, the same restrictions and
limitations exist as in a cable environment where a third-party cable modem is used.
Figure 5-10 Cable QoS with a Third-party Modem
For the third-party modem solution (illustrated in
·
The IP phone handles classification of the VoIP bearer and control traffic. The IP phone marks its
traffic at Layer 2 with a CoS of 5 for bearer traffic and 3 for control traffic. It marks its traffic at
Layer 3 with a DHCP PHB label of EF for bearer traffic and AF31 for control traffic.
·
A Cisco 806 or 1710, or equivalent router, provides preferential scheduling for the VoIP bearer and
control traffic that has been classified or tagged by the IP phone.
·
LLQ/CBWFQ is used to give the preferential treatment.
·
The router also shapes its traffic to the guaranteed bandwidth that the service provider is delivering.
There are many factors that are out of our control when you do not directly terminate the cable
connection.
illustrates the best that can be done in this environment.
Example 5-4
Cable QoS Configuration with a Third-party Modem
class-map match-any CBS-256kbps
match any
class-map match-all VOICE
match ip dscp EF
class-map match-all VOICE-CONTROL
match ip dscp AF31
!
policy-map WAN-EDGE
class VOICE
priority percent 33
class VOICE-CONTROL
bandwidth percent 2
class class-default
fair-queue
random-detect dscp-based
IP
IP
IP
Two-box
Third-party modem
Single-box
Cisco
806/1710
Cisco 9x5
PIX 501
Cable
backbone
To head
end
74927
