5-7
Cisco AVVID Network Infrastructure Enterprise Quality of Service Design
956467
Chapter 5 QoS in a SOHO Virtual Private Network for IP Telephony
Solutions
One and Two Box DSL Solution
The one-box and two-box solutions require the same set of features from a QoS perspective. The only
difference is that in a one box solution, VPN and QoS are in the same box and a two box solution, the
VPN functionality is moved out of the DSL termination device. In both of these solutions (where QoS
is being provided by the DSL termination devices), all three aspects of QoS must be provided:
classification, scheduling (including LFI and traffic shaping), and provisioning.
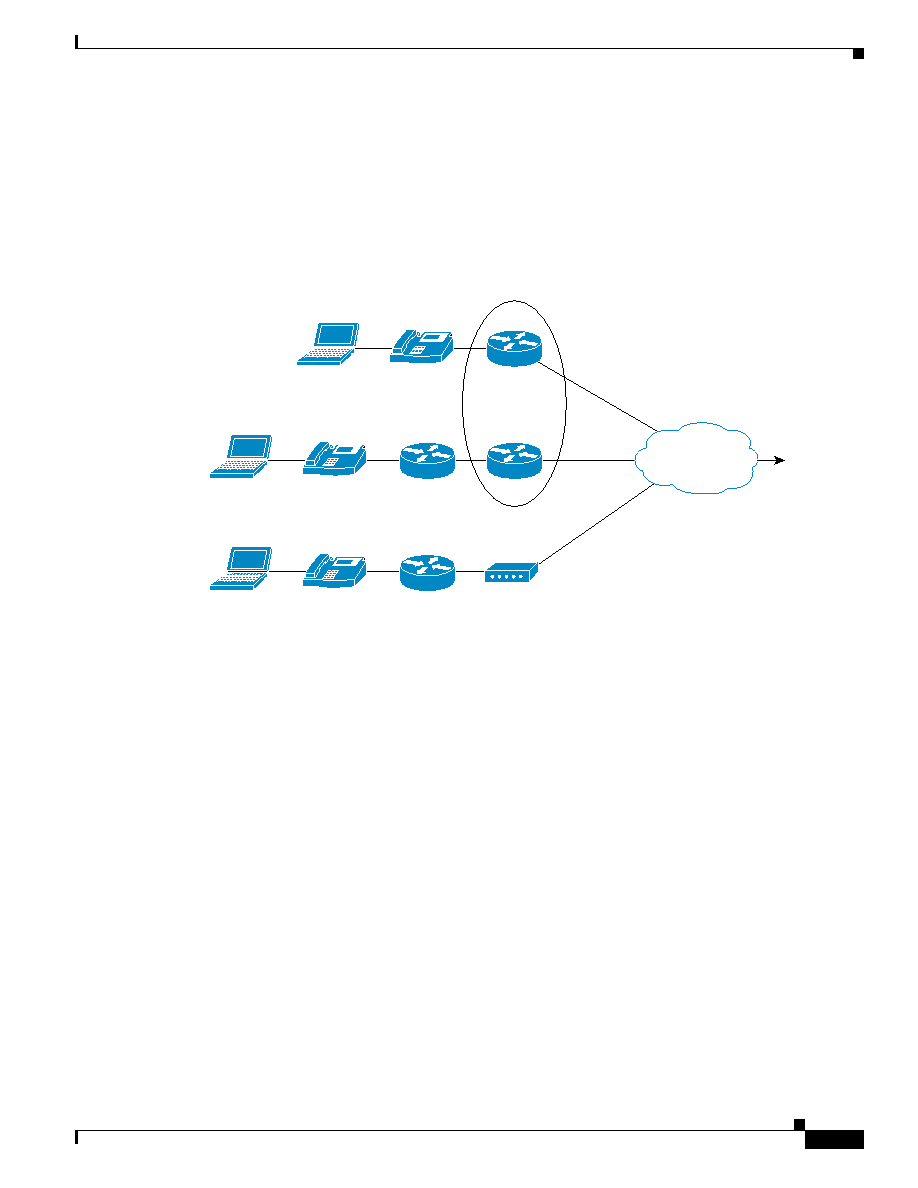
Figure 5-5
One- and Two-Box DSL Deployments
For the one- and two-box DSL solutions (illustrated in
·
The IP phone handles classification of the VoIP bearer and control traffic. The IP phone marks its
traffic at Layer 2 with a CoS of 5 for bearer traffic and 3 for control traffic. It marks its traffic at
Layer 3 with a DHCP PHB label of EF for bearer traffic and AF31 for control traffic.
·
A Cisco 827, or equivalent router, handles scheduling.
·
LLQ/CBWFQ is used to give the VoIP bearer and control traffic the guarantees for loss, delay, and
delay variation that they require.
shows the IOS configuration used to address the QoS requirements for VoIP in a SOHO
environment.
Example 5-1
DSL PPPoA QoS Configuration
class-map match-all VOICE
match ip dscp EF
class-map match-all VOICE-CONTROL
match ip dscp AF31
!
policy-map TELEWORK
class VOICE
priority 64
class VOICE-CONTROL
bandwidth 8
class class-default
fair-queue
IP
IP
IP
Two-box
Third-party modem
Single-box
3rd-party
DSL modem
Cisco
806/1710
Cisco 827
PIX 501
DSL
Backbone
To head
end
74922
