36
Chapter 1
Internetworking
802.2 Logical Link Control (LLC) Header
Dest. SAP: 0xAA SNAP
Source SAP: 0xAA SNAP
Command: 0x03 Unnumbered Information
Protocol: 0x080007809B AppleTalk
You can identify a SNAP frame because the DSAP and SSAP fields are
always AA, and the Command field is always 3. This frame type was created
because not all protocols worked well with the 802.3 Ethernet frame, which
didn't have an Ether-Type field. To allow the proprietary protocols created
by application developers to be used in the LLC frame, the IEEE defined the
SNAP format. Up until last year or so, the SNAP frame was on its way out
of the corporate market. However, the new 802.11 wireless LAN specifica-
tion uses an Ethernet SNAP field to identify the Network layer protocol.
Cisco also still uses a SNAP frame with their proprietary protocol Cisco Dis-
covery Protocol (CDP)--something I'm going to talk about in Chapter 7.
Ethernet at the Physical Layer
Ethernet was first implemented by a group called DIX (Digital, Intel, and
Xerox). They created and implemented the first Ethernet LAN specification,
which the IEEE used to create the IEEE 802.3 Committee. This was a
10Mbps network that ran on coax, twisted-pair, and fiber physical media.
The IEEE extended the 802.3 Committee to two new committees known
as 802.3U (FastEthernet) and 802.3Z (Gigabit Ethernet). These are both
specified on twisted-pair and fiber physical media.
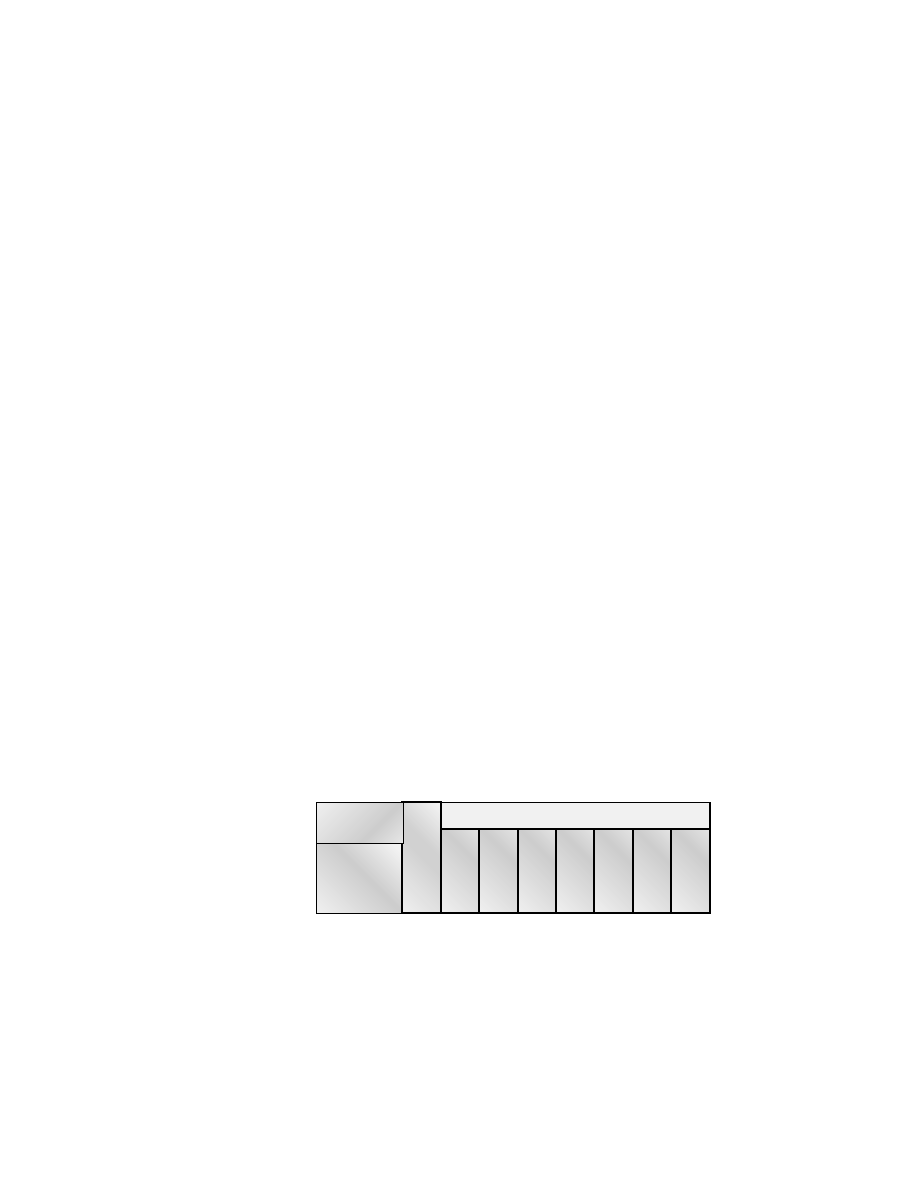
Figure 1.14 shows the IEEE 802.3 and original Ethernet Physical layer
specifications.
F I G U R E 1 . 1 4
Ethernet Physical layer specifications
When designing your LAN, it's really important to understand the differ-
ent types of Ethernet media available to you. Sure, it would certainly be great
to run Gigabit Ethernet to each desktop and 10Gbps between switches, and
Data Link
(MAC layer)
Physical
Ethernet
802.3
10Base2
10Base5
10BaseT
10BaseF
100BaseTX
100BaseFX
100BaseT4
Copyright ©2002 SYBEX, Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
