network traffic.
dles error notification, network topology, and flow control. This means the
Data Link layer will ensure that messages are delivered to the proper device
on a LAN using hardware addresses, and translates messages from the Net-
work layer into bits for the Physical layer to transmit.
and source address. This added information forms a sort of capsule that sur-
rounds the original message in much the same way that engines, navigational
devices, and other tools were attached to the lunar modules of the Apollo
project. These various pieces of equipment were useful only during certain
stages of space flight and were stripped off the module and discarded when
their designated stage was complete. Data traveling through networks is similar.
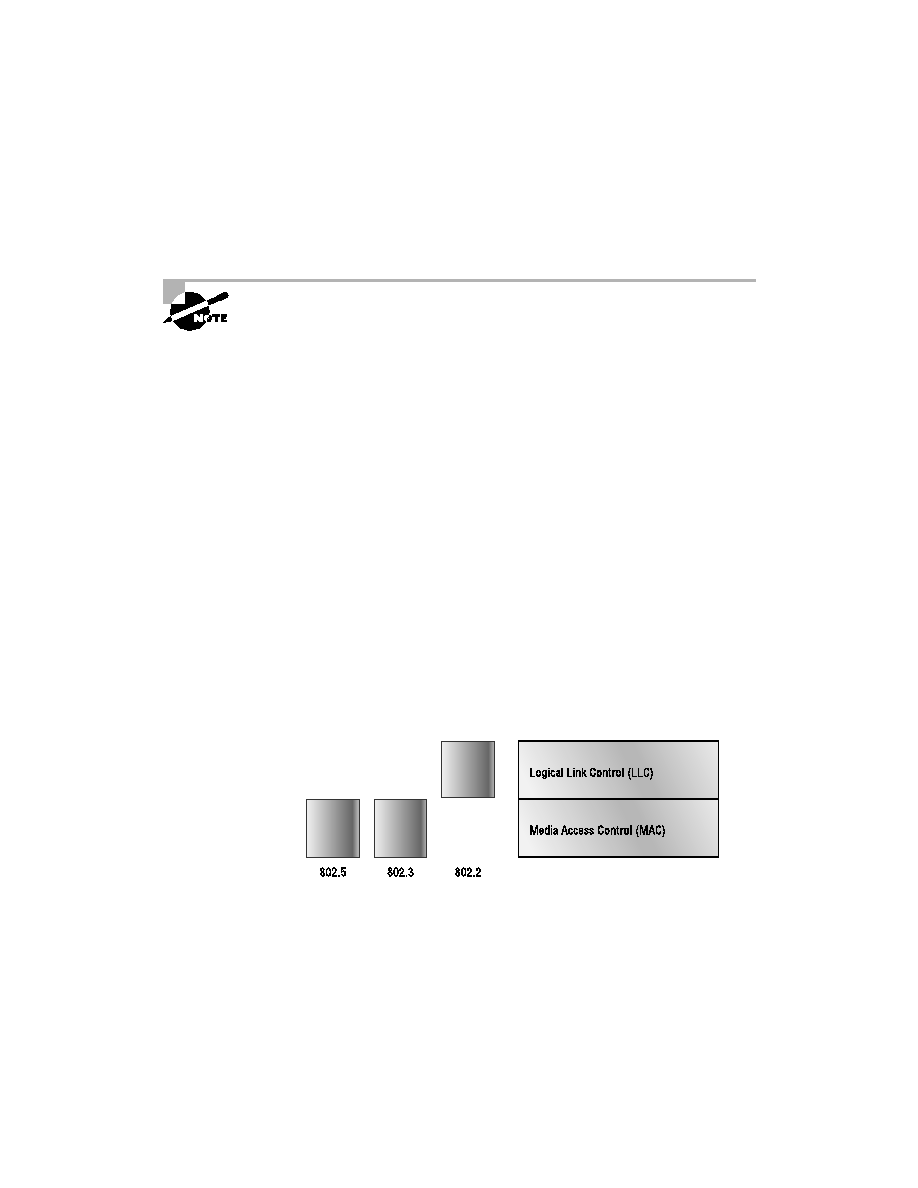
used in conjunction with and adds functionality to the other IEEE standards.
only concerned about where networks are located, and the best way to reach
them--including remote ones. Routers are totally obsessive when it comes to