414
Chapter 8
Configuring Novell IPX
F I G U R E 8 . 2
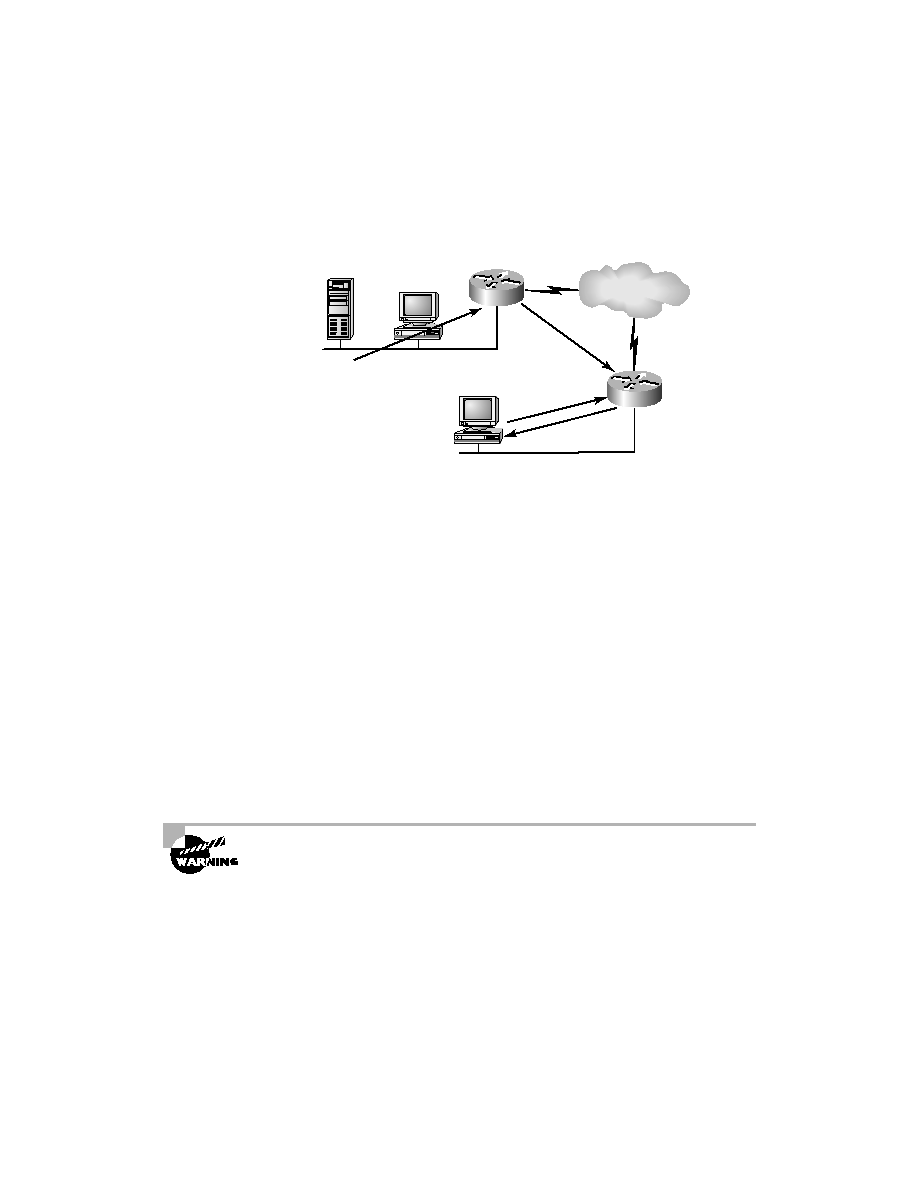
Remote IPX clients on a serverless network
This communication insulates the client from the task of locating and
tracking available network resources; it places that burden on the server
instead. The client simply broadcasts a GNS and waits for a reply. From the
client's perspective, all network resources respond as though they were local,
regardless of their physical location in the internetwork.
Server-Server Communication
Communication between two NetWare servers is a bit more complicated
than client-server communication. As mentioned earlier, servers are respon-
sible for maintaining tables of all available network resources, regardless of
whether those resources are local to the server. Also, keep in mind that each
server must be able to locate
any
resource on the internetwork.
Servers exchange two types of information using two separate protocols:
SAP (Service Advertising Protocol) and RIP (Routing Information Protocol).
As their names suggest, SAP communicates service information, and RIP
communicates routing information.
Please don't confuse RIP in IPX with RIP in TCP/IP. They're both routing
protocols, but they're not the same routing protocol.
Service Advertising Protocol
NetWare servers use SAP to advertise the services they offer by sending out
an SAP broadcast every 60 seconds. The broadcast includes all services that
the server has learned about from other servers--not just the ones they
NetWare
file server
SAP
SAP
GNS request
GNS reply
Router A
Router B
Copyright ©2002 SYBEX, Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
