134
Chapter 3
Internet Protocols
send, it must inform a Network Access protocol, such as Ethernet or Token
Ring, of the destination's hardware address on the local network. (It has
already been informed by upper-layer protocols of the destination's IP
address.) If IP doesn't find the destination host's hardware address in the
ARP cache, it uses ARP to find this information.
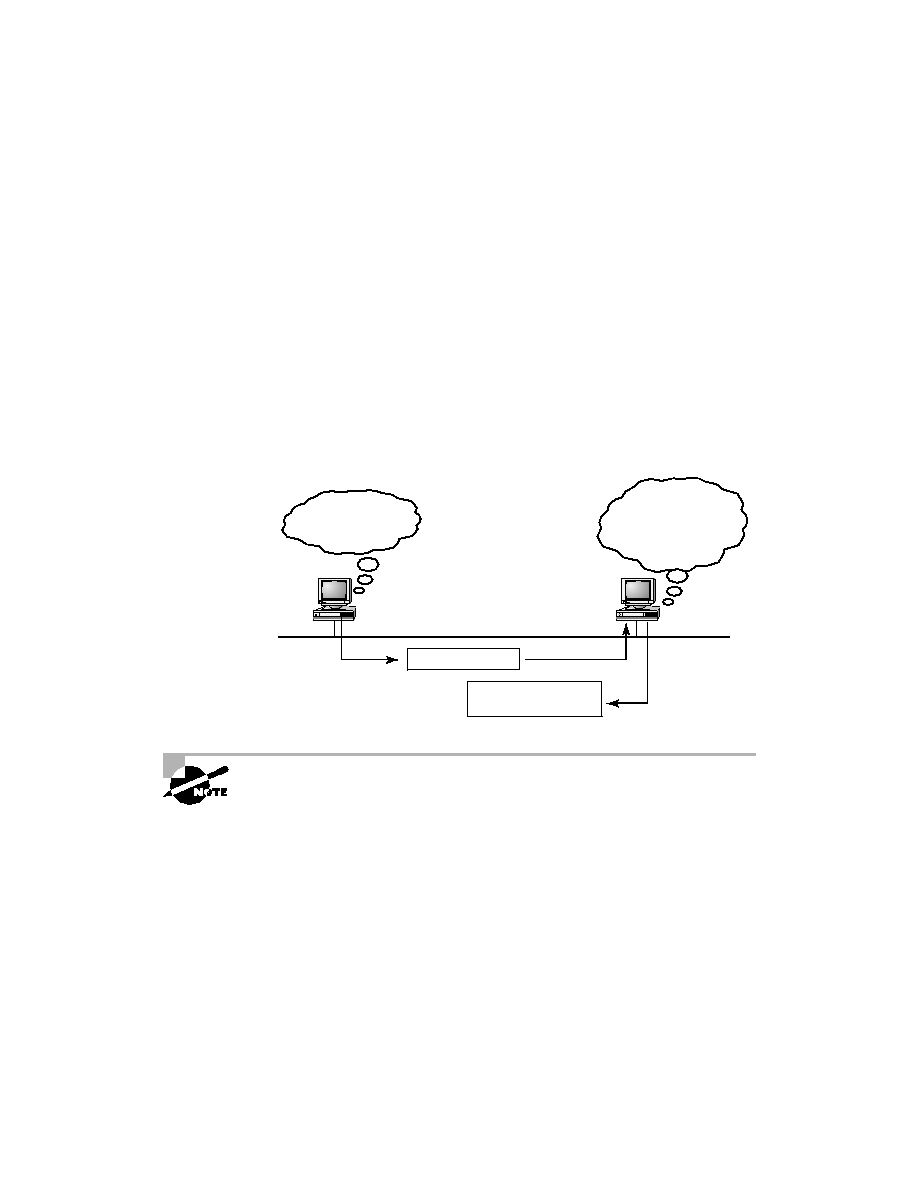
As IP's detective, ARP interrogates the local network by sending out a
broadcast asking the machine with the specified IP address to reply with its
hardware address. In other words, ARP translates the software (IP) address
into a hardware address--for example, the destination machine's Ethernet
board address--and from it, deduces its whereabouts. Figure 3.8 shows how
an ARP looks to a local network.
F I G U R E 3 . 8
Local ARP broadcast
ARP resolves IP addresses to Ethernet addresses.
The following trace shows an ARP broadcast. Notice that the destination
hardware address is unknown, and is all Fs in hex (all 1s in binary), and
a hardware address broadcast.
Flags: 0x00
Status: 0x00
Packet Length: 64
Timestamp: 09:17:29.574000 01/04/2002
I need the Ethernet
address of 10.1.1.2
I heard that broadcast.
The message is for me.
Here is my Ethernet address.
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.2
IP: 10.1.1.2 = ???
IP: 10.1.1.2
Ethernet: 4523.7985.7734
Copyright ©2002 SYBEX, Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
