92
Chapter 2
Layer-2 Switching
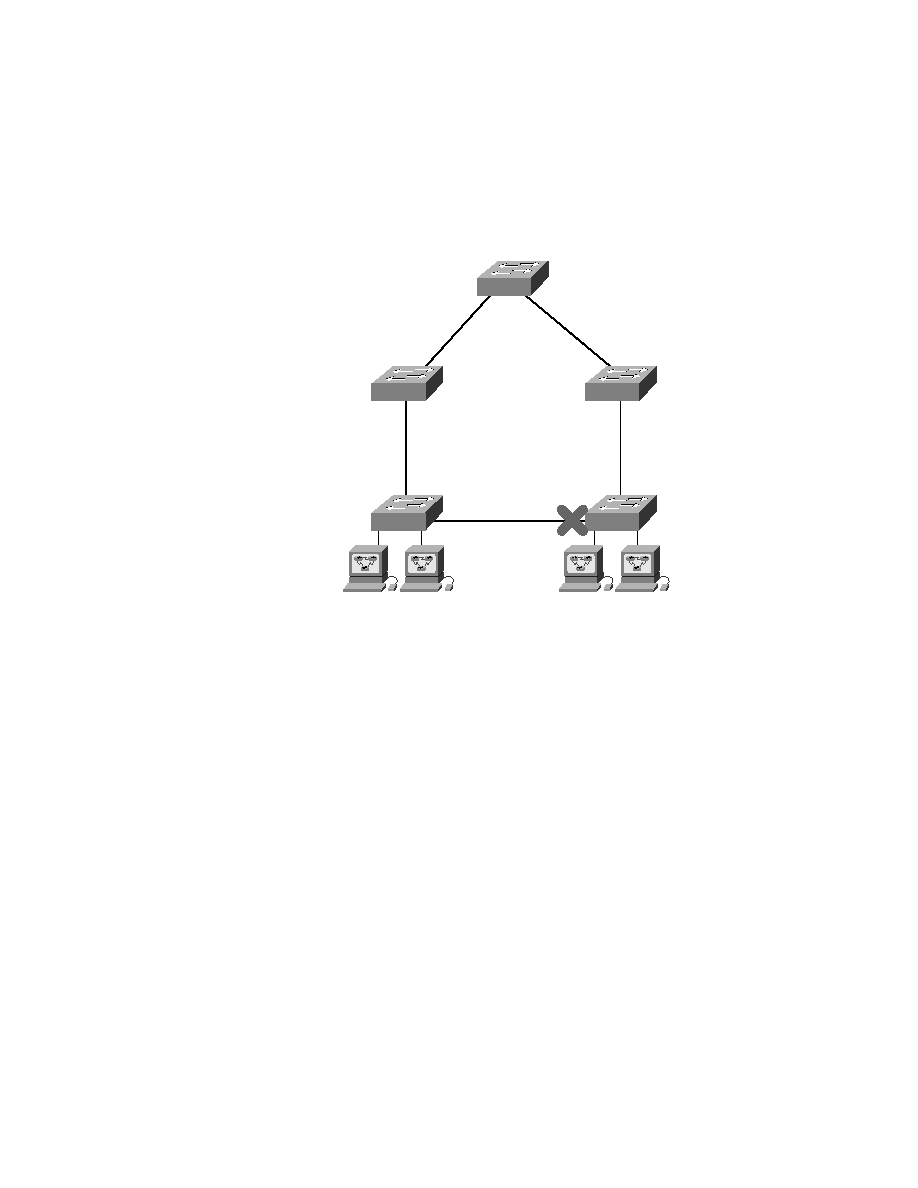
F I G U R E 2 . 9
Spanning tree example answers
Since Switch A has the lowest MAC address and all five switches use the
default priority, Switch A gets to be the root bridge. And remember this:
A root bridge always has every port in forwarding mode (designated
ports).
To determine the root ports on Switch B and Switch C, just follow the
connection to the root bridge. Each direct connection to the root bridge will
be a root port, so it will become designated. On Switches D and E, the ports
connected to Switches B and C are Switches D and E's closest ports to the
root bridge (lowest cost), so those ports are root ports and in forwarding
mode (designated).
Take another look at the Figure 2.9. Can you tell which of the ports
between Switch D and E must be shut down so a network loop doesn't
occur? Let's work it out: Since the connection from Switches D and E to
Switches B and C are root ports, those can't be shut down. Next, the bridge
ID is used to determine designated and nondesignated ports; so, because
Switch D has the lowest (best) bridge ID, Switch E's port to Switch D will
become nondesignated (blocking), and Switch D's connection to Switch E
will be designated (forwarding).
Switch A
MAC = 0000.8c00.1201
All ports designated
(forwarding)
Root bridge
Switch C
MAC = 0000.8c00.1202
designated
(forwarding)
Root port
Switch B
designated
(forwarding)
MAC = 0000.8c00.8955
Root port
Switch E
MAC = 0000.8c00.9870
nondesignated
(blocking)
Root port
Switch D
designated
(forwarding)
MAC = 0000.8c00.2101
Root port
Copyright ©2002 SYBEX, Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
