ISDN Protocols and Design 569
A tool to help you remember the specifications and layers is that the second digit in the Q-series
matches the OSI layer. For example, in ITU-T Q.920, the second digit, 2, corresponds to OSI
Layer 2. In the I-series, the second digit of the specification numbers is two more than the
corresponding OSI layer. For example, I.430, with the second digit of value 3, defines OSI
Layer 1 equivalent functions.
LAPD is used to deliver signaling messages to the ISDN switch--for example, a call setup
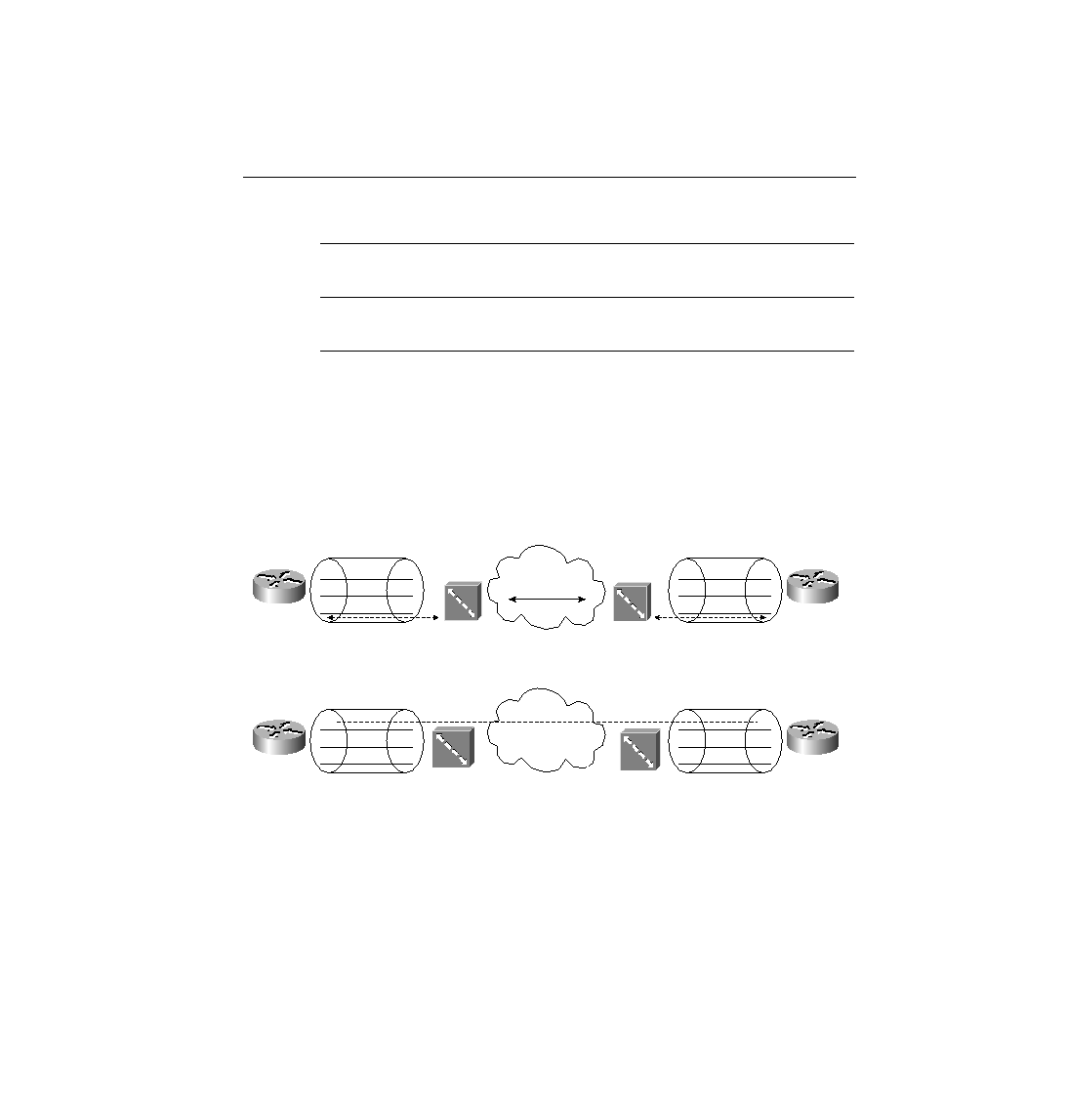
message. Figure 8-21 shows the use of LAPD versus PPP on B channels.
Figure 8-21
LAPD and PPP on D and B Channels
The call is established through the service provider network; PPP is used as the data link
protocol on the B channel from end to end. LAPD is used between the router and the ISDN
switch at each local central office (CO) and remains up so that new signaling messages can be
sent and received. Because the signals are sent outside the channel used for data, this is called
out-of-band signaling.
The BRI encodes bits at 192 kbps, with most of the bandwidth (144 kbps) being used for the
two B channels and the D channel. The additional bits are used for framing.
3
ITU-T I.450
ITU-T I.451
ITU-T Q.930
ITU-T Q.931
Defines signaling messages--for
example, call setup and takedown
messages
Table 8-26
ISDN I-Series and Q-Series Mentioned in ICND and ITM: OSI Layer Comparison (Continued)
Layer, as
Compared to OSI
I-Series
Equivalent
Q-Series
Specification
General Purpose
Fred
Fred
Barney
B0
B1
D
BRI
BRI
LAPD
B0
B1
D
BRI
LAPD
Call Setup
Flows
Call Setup
Flows
Call Setup
Flows
Barney
B0
B1
D
LAPD
B0
B1
D
BRI
LAPD
PPP
ch08.fm Page 569 Monday, March 20, 2000 5:17 PM
