Cisco's desire that the professional certifications prove that the candidate knows how to make
networks that work rather than to certify individuals who are willing to memorize just for the
sake of passing the test. However, IPX encapsulation is one area in which memorization is
important once the base concepts are understood. Table 5-32, later in this section, lists several
terms you should remember.
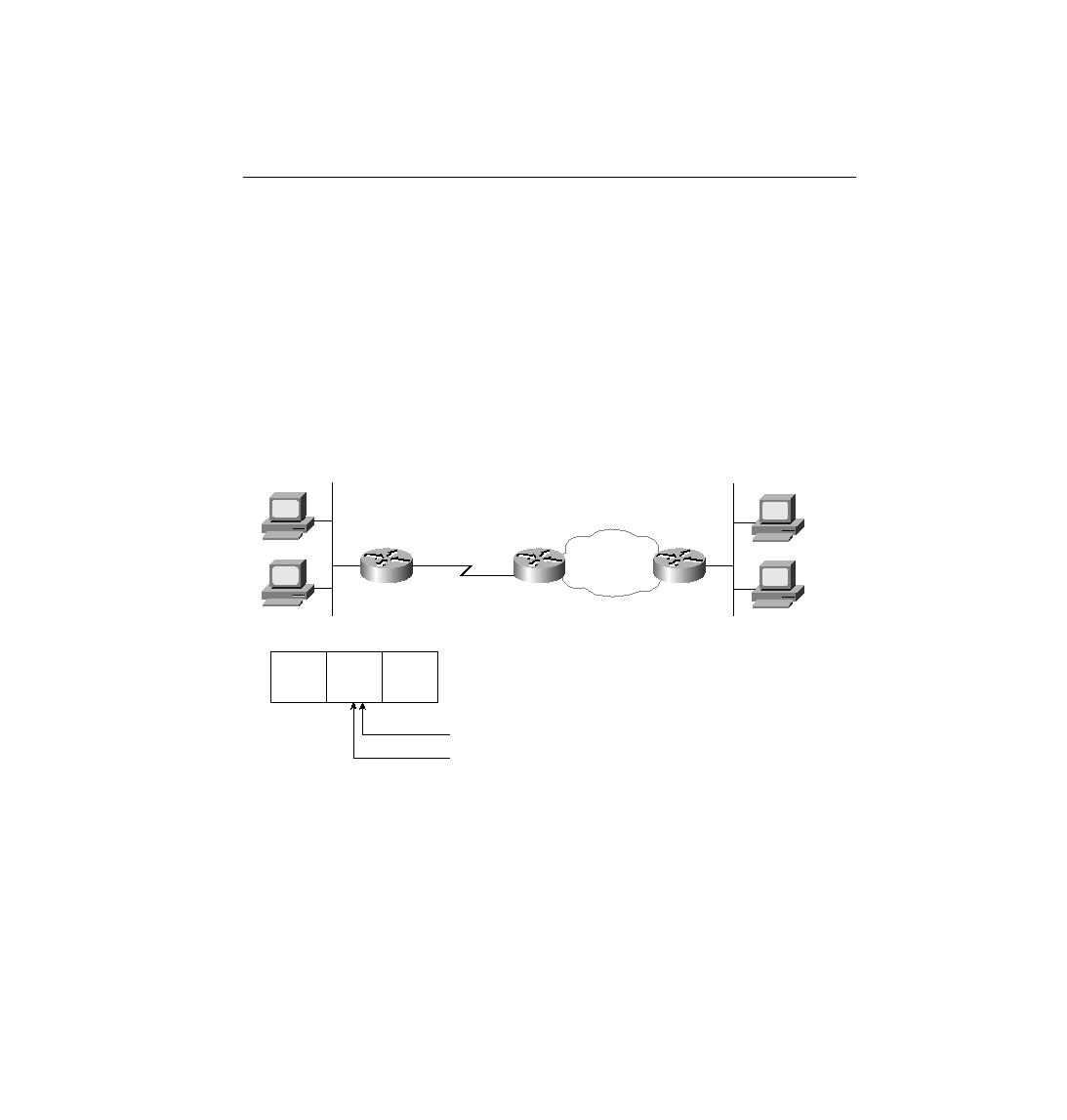
related to routing, as seen using Figure 5-34. NetWare servers use internal network numbers.
Also, clients, servers, and routers all must be configured to use the correct encapsulation.
Routing will also be reviewed using the same figure.
servers use an internal network number, the destination of packets from Client 1 to Server 1 is
1000.0000.0000.0001. The source address of these packets is Client 1's IPX address
Server 2 internal net 1001
Server 1 MAC 0200.AAAA.AAAA
Server 2 MAC 0200.BBBB.BBBB