typically full-duplex (four-wire) circuits. In other words, either endpoint can send at any time.
the Frame Relay switch. These links are also typically full-duplex links, so no arbitration is
needed. The Frame Relay network is shared among many data terminal equipment (DTE)
devices, whereas the access link is not shared, so arbitration of the medium is not an issue.
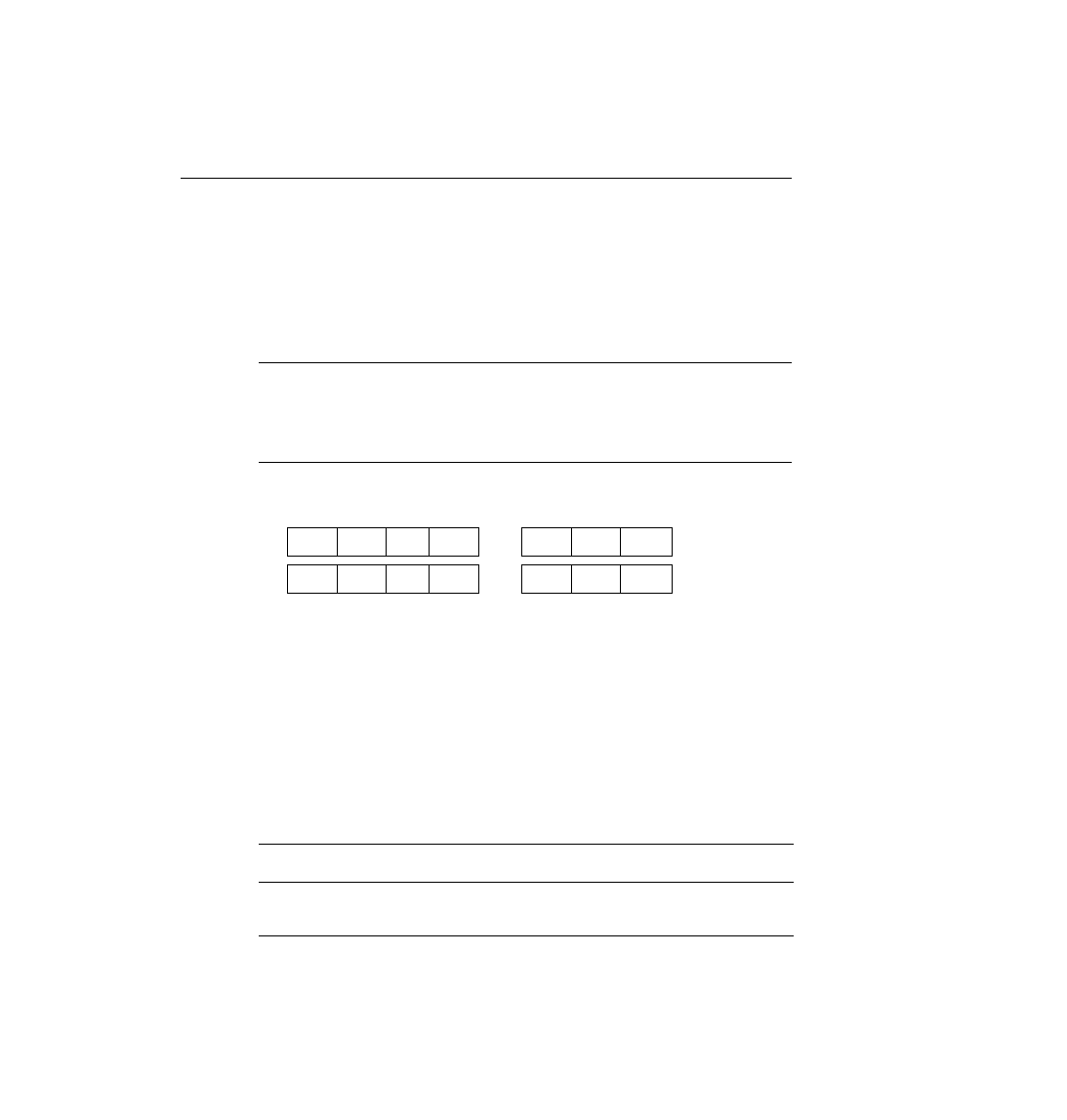
As used in this book and in the ICND course, the word frame refers to particular parts of the
data as sent on a link. In particular, frame implies that the data link header and trailer are part
of the bits being examined and discussed. Figure 3-11 shows frames for the four data link
protocols.
addresses. Addressing is needed on LANs because there can be many possible recipients of
data--that is, there could be more than two devices on the link. Because LANs are broadcast
media--a term signifying that all devices on the media receive the same data--each recipient
must ask the question, "Is this frame meant for me?"
(MAC) addresses, which are 6 bytes long and are represented as a 12-digit hexadecimal
number. Table 3-7 summarizes most of the details about MAC addresses.
Features
Ring) are the MAC sublayers of these two LAN data link
protocols.