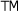10.8. Character Entity References
Characters not found in the normal alphanumeric character set, such as < and &, must be specified in HTML using character entities. Using the standard desktop publishing keyboard commands (such as Option-g for the © symbol) within an HTML document will not produce the desired character when the document is rendered in a browser. In fact, the browser generally displays the numeric entity for the character.
Character entities can be referenced by name (&name;) or by numeric value (&#nnn;). The browser interprets the string to display the proper character. Named entities are preferable because numeric values may be interpreted differently on different platforms.
Table 10-3 presents the character entities for commonly used special characters. The complete list appears in Appendix F, "Character Entities".
Table 10-3. Common special characters and their character entities
|
Character |
Description |
Name |
Number |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Character space (nonbreaking space) |
  |
||
|
& |
Ampersand |
& |
& |
|
< |
Less-than sign (useful for displaying tags on a web page) |
< |
< |
|
> |
Greater-than sign (useful for displaying tags on a web page) |
> |
> |
|
" |
Left curly quotes (nonstandard entity) |
(none) |
“ |
|
" |
Right curly quotes (nonstandard entity) |
(none) |
” |
|
|
Trademark (nonstandard entity) |
(none) |
™ |
|
£ |
Pound symbol |
£ |
£ |
|
¥ |
Yen symbol |
¥ |
¥ |
|
© |
© |
© |
|
|
® |
® |
® |

Copyright © 2002 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.